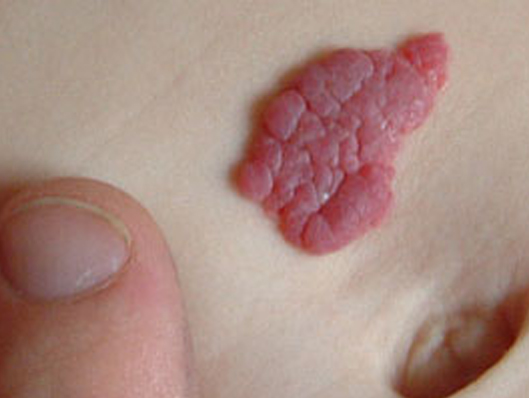
Hemangioma is popularly known as a birthmark. These are benign tumours present on the skin caused by abnormal accumulation of dense cluster of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells are the ones who line the blood vessels internally.
Haemangioma occurs mostly in premature babies and infants. The exact cause of this medical condition is still unknown.
In the first two weeks, the growth happens, and then they rapidly enlarge during the first year. However, the growth slows down and finally stops by 6 to 7 years of age. A small amount of thin residual skin or fatty tissue may stay after involution.
Hemangiomas can be external or deep within and usually show certain symptoms. The bright red, raised or flat patches on the skin may be indications of superficial Hemangioma. However, the deep ones do not have an outward appearance on the skin and grow below the surface. Both the types are compressible when felt. The size of the cluster is variable and mostly appears in the neck region or even on the head.
Hemangonias are usually non-problematic, but if they occur in major organs and obstructs them, immediate treatment is needed. Hemangonias can be cured by surgical removal, using drugs or steroids or even blood vessel embolization. Embolization is the technique of injecting foreign substances into the vessels that stop the blood flow.
Usually, hemangiomas are very simply detected without using any clinical testing method as they can be very easily seen with naked eyes. However, ultrasound, MRI or even CT Scans may be needed for the deeper lesions.
Plastic Surgen , Dr. Sandeep Kansal is a consultant Plastic-cosmetic Surgeon in Meerut. He is currently practicing at , Kailashi Superspeciality , Lokpriya And Nuteema Hospital in Meerut.
Copyright © 2023 Dr Sandeepkansal. All Rights Reserved.