Maxillofacial surgery, also known as oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMS), is a specialized branch of surgery that focuses on the diagnosis and surgical treatment of conditions affecting the head, face, jaws, and mouth. It is a field that combines elements of dentistry, medicine, and surgery to address a wide range of conditions, including congenital anomalies, traumatic injuries, and various pathologies affecting the oral and facial regions.
Key aspects of maxillofacial surgery include:
Oral and Dental Procedures:
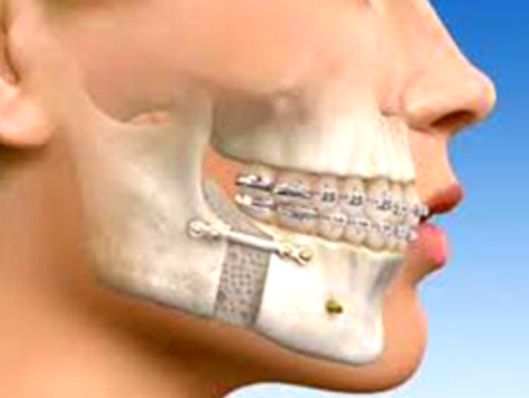
Orthognathic Surgery:
Facial Trauma Reconstruction:
Cleft Lip and Palate Repair:
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
Head and Neck Pathology:
Sleep Apnea Surgery:
Cosmetic Facial Surgery:
Maxillofacial surgeons undergo extensive training, which includes dental and medical education, as well as residency training in oral and maxillofacial surgery. They are often involved in multidisciplinary teams, collaborating with other healthcare professionals, including orthodontists, plastic surgeons, and otolaryngologists, to provide comprehensive care for patients with complex facial conditions.
Plastic Surgen , Dr. Sandeep Kansal is a consultant Plastic-cosmetic Surgeon in Meerut. He is currently practicing at , Kailashi Superspeciality , Lokpriya And Nuteema Hospital in Meerut.
Copyright © 2023 Dr Sandeepkansal. All Rights Reserved.